Today's Technology Advancements Shaping Tomorrow's Smart Transportation
By Jim Misener | Senior Director, Product Management, Qualcomm Technologies
Technology advances in cellular communication have ushered an era of ubiquitous connectivity. Smart transportation is about disseminating information about the transportation network from an underlying network of sensors, infrastructure, and communication devices to build operating solutions and services for an intelligent transport system (ITS): an ITS which is safe, efficient, inclusive, and serves the societal needs of modern living will need to reap the benefits of both the cellular and the transportation network. The ITS rubric is broad, and we at Qualcomm Technologies provide solutions across the board ─ from connectivity and telematics to in-vehicle compute, which are key to autonomous vehicles. Road owners and users alike benefit from unparalleled set of tools for personal mobility, safety, and environmentally-friendly transportation services, up to and including automated driving.
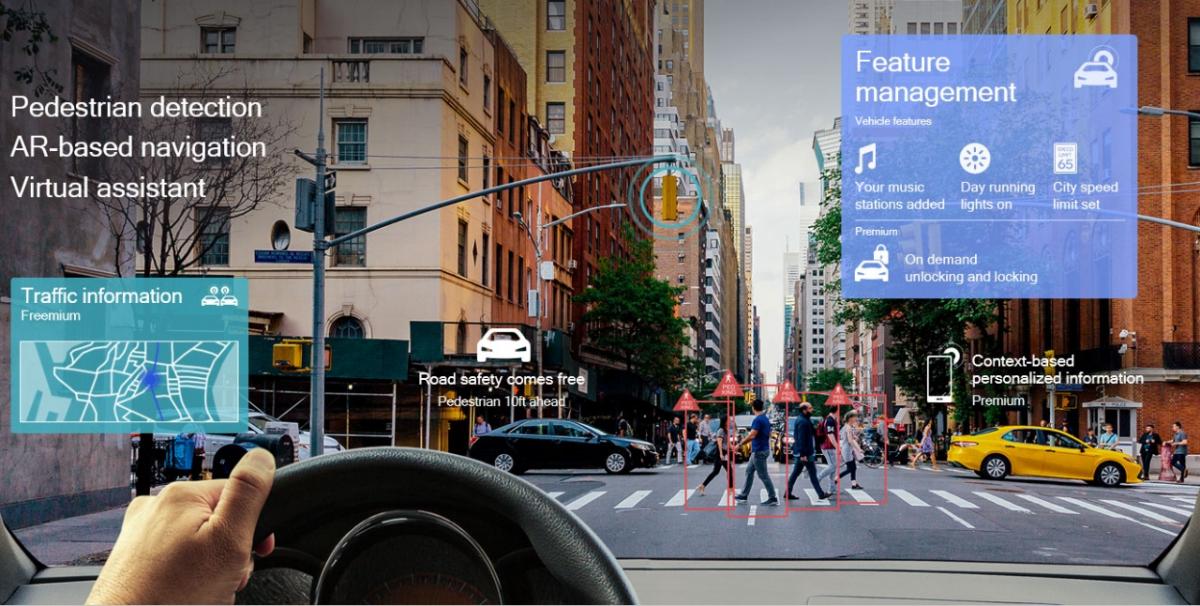
ITS empowers its users with meaningful information, facilitating a wide range of services from pre-trip planning and en route information, to advanced road safety services and paving the path to enhanced automated driving. While such applications bring obvious benefits to road users, they also provide actionable insight to private entities such as transportation planners working alongside government agencies on optimal operations strategies. Transportation planners can use the information to project travel demand. The demand information can help to determine optimal deployment of transportation infrastructure, advanced public transit services, and placement of ITS-enabled transportation pricing and demand management systems such as electronic toll collection or variable parking fees. Planners can also benefit from insights into arterial road usage, traffic conditions, and congestion reports in shaping our neighborhoods and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Importantly, according to the World Health Organization1, approximately 1.35 million people lose their lives each year to road traffic crashes, and more than half of all road fatalities are among vulnerable road users such as pedestrians, bike riders, motorcyclists, etc. In a smart transportation system, we need vehicles not just to reliably communicate with each other but also with the road infrastructure. The traffic management center (TMC) which oversees overall traffic control of the city or region can be hosted in a central cloud that harnesses the information from a wide distribution of edge clouds located throughout the city. Vehicular networks are highly dynamic, so it is essential for edge servers to be located closer to the real action providing local analytics, context, and faster processing.
Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication thus becomes imperative for a comprehensively integrated ITS, which complements the growing network of connected vehicles exchanging information and greatly improving road safety. Our team of engineers at Qualcomm Technologies is aggressively working on Cellular-Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X), a core technology underpinning an evolving smart transportation framework of connected vehicles and road infrastructure. C-V2X, which includes vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), uses a direct communication mode or sidelink without relying on the cellular network. Vehicle-to-network (V2N) communication, on the other hand, requires participation from the mobile network operators (MNOs) to provide services through the cellular network to vehicles and other vulnerable road users. V2N has been available roughly for over two decades now, supporting various telematics and traffic applications.
Integrating C-V2X with the V2N network can deliver measurable safety and traffic benefits, in addition to significant economic benefits to all stakeholders. By granting roadside access to MNOs, transportation planners and road operators can share the cost of equipping our roads with infrastructure nodes, called Road Side Units (RSUs). At the same time, MNOs can benefit from getting roadside access for additional small cells installation to expand their cellular coverage. Public-private partnerships can thus go a long way in creating smart transportation solutions which are economically feasible and sustainable. At Qualcomm Technologies, we have been working closely with several organizations including multiple Departments of Transportation (DoT), metropolitan organizations, local agencies, and technology providers to build unique solutions around C-V2X as a first step towards an ITS of the future.
To support an ITS of connected vehicles, roads, and infrastructure, we envision the need for car-to-cloud services to provide efficient application, content, and service management. With our Qualcomm car-to-cloud platform, we enable on-demand soft SKU configuration and over-the-air software updates making feature licensing and device management scalable. Such enhancements open up possibilities to a wide range of multi-tiered streaming, location-based, and personalization experiences and services for users.
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, about 90% of motor vehicle crashes can be attributed at least in part to human error. Automotive companies and Tier 1 OEMs have a real opportunity to lead with autonomous or self-driving vehicles to drastically reduce human error led accidents for increased road safety. Our system approach of building an autonomy stack greatly leverages our proven AI capabilities that focusses on perception, planning, action, and connectivity for autonomous driving. The Qualcomm Snapdragon Ride platform is equipped with hybrid deep learning and computer vision to provide maximum performance of up to 700+ TOPs, supported by much simpler but innovative air-cooling vs. a complex liquid cooling system. This is just one of the several examples in how we design end-to-end solutions through our technology leadership in our products.
The proliferation of smartphones has contributed immensely to the rising expectations of enhanced personal mobility choices. There is a strong connection between personal mobility and economic mobility. This is where mobility on demand such as bus rapid transit and various other shared ride services have the potential to revolutionize transportation systems by maximizing automation opportunities by providing personal mobility services which are ─ safer, affordable, reliable, and available to all.
3GPP Releases 14 and 15 introduced the direct communication mode or sidelink, delivering latency-sensitive basic safety applications using C-V2X, without relying on the cellular network. As we continue to innovate on 5G NR technologies, Release 16+ sidelink brings several enhancements in the form of higher throughput, lower latency, and enhanced reliability. All of these are expected to greatly enhance autonomous driving through perception sharing, path planning, real-time local updates, and coordinated driving. These features facilitate the next generation of ITS solutions for multiple autonomous driving applications such as fleet management systems, advanced driver assistance systems, mobility, and parking services, in addition to greatly reducing emissions for a cleaner environment.
At the heart of our smart transportation vision lies an integrated communication and transportation network that brings several societal benefits. Through our thought leadership, strong 5G roadmap, proven AI capabilities, and a host of other enabling technologies such as advanced positioning, extended reality, multi-mode modem and RFFE, power management, Wi-Fi/Bluetooth, etc., we are shaping a new era of smart transportation for advanced road safety, enhanced personal mobility, and environmental sustainability.
To learn more about our work today on building an ITS of the future, join me in this webinar: How are today’s technology advancements creating tomorrow’s smart transportation system?
Visit our web page to find additional C-V2X and smart transportation information
1. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/road-traffic-injuries